
Contact Center as a Service
Discover how cloud-based Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS) enhances customer support, lowers IT costs, and enables seamless omnichannel communication.
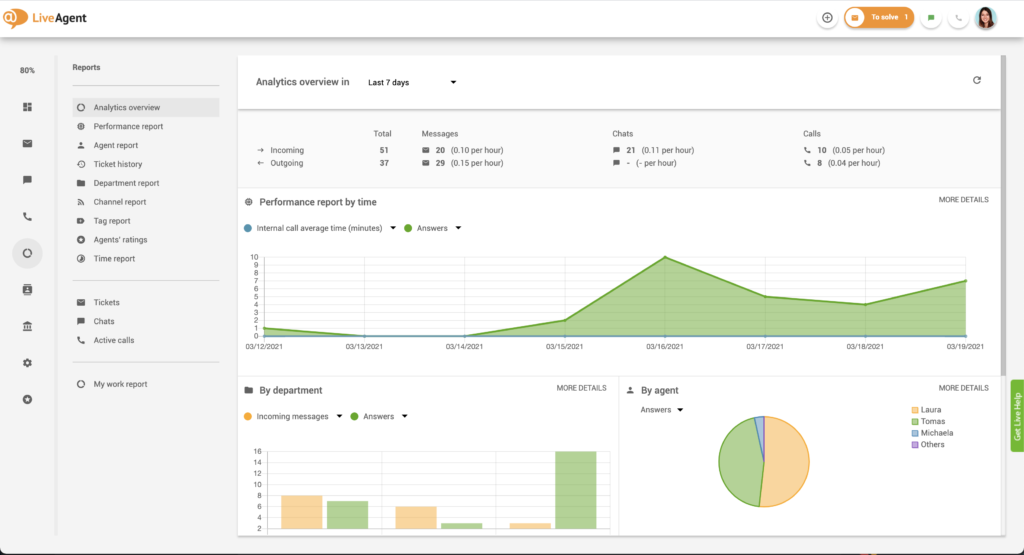
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud model offering tools for app development, infrastructure, database management, and more in an online environment.
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud model offering tools for app development, infrastructure, database management, and more in an online environment. It enables developers to create, deploy, and manage applications efficiently without managing backend systems.
Cloud computing is taking over the business landscape, and Platform as a Service is gaining in popularity. Like all other cloud models, PaaS also involves subscribing and using it whenever needed.
However, companies can use this option to create any sort of application they can imagine using a development & deployment platform in the cloud. Cloud providers have diversified services that are focused on B2B, not just B2C.
Along with Software as a Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), it is a cloud computing model that lets you develop, maintain, and deliver an application. Traditionally these were separate, and even if companies could get a full suite, they would have to install and store them on local devices. With these solutions, users can code and deploy directly to the cloud.
The all-in-one solution helps developers consolidate app deployment and their developer tools at the same time. It saves time by using premade components. Additionally, various integrations allow them to collect valuable business analytics.
Like other cloud services, PaaS comes with underlying infrastructure, networking, storage, and servers. The system also allows developers to create different types of apps, including ones that use middleware, database management, software deployment, and intelligence services.
PaaS solutions have everything a modern company could need for software applications and infrastructure management. When it comes to servers, you can find solutions with physical or virtual servers, as well as a remote server and an email server.
Comprehensive database management systems, along with a wide range of database management tools, deployment tools, and environments, can help any development process regardless of the approach or the end goal.
PaaS systems power the back end of an application, including storage, operating systems, servers, and databases. In other words, developers get the tools and the environment to build their applications on a pre-existing back end.
Developers can work from any device, anywhere, and anytime with managed load balancing. This kind of setup allows developers to focus on user experience and the front-end. The whole environment also comes with continuous integration to provide extra functionality.
Providers of the PaaS environment apply security patches and maintain the platform as a whole. By using these sorts of environments, security risks are reduced, and development becomes more targeted.
PaaS solutions can be divided into countless categories. However, there are three major types that you should know:
These solutions can be free and open source. You can use them as completely independent and separate platforms providing lots of flexibility. In most cases, they are ideal for hybrid PaaS cloud options.
Characteristics:
This kind of solution is tied closely to SaaS platforms that are used often, such as Intuit, Salesforce, and so on. These PaaS solutions create an ecosystem around a specific SaaS app for developers to add new capabilities that run on the core app.
Characteristics:
In most cases, these are IaaS vendors that provide PaaS capabilities. Even though they might not have the same functionalities, it can be a good option for users looking to commit to a particular IaaS. However, these PaaS systems have the potential for vendor lock-in.
Characteristics:
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is the most popular PaaS solution. The great thing about it is that it allows IaaS users to build apps, and there are constantly new development tools being added. AWS Elastic Beanstalk is ideal for apps developed in Docker, Java, PHP, Python, and other programming languages.
Key Features:
IBM offers an open-source security platform with total control over the complete web application lifecycle. DevOps teams can utilize lots of different third-party service provider options extending functionalities.
Key Features:
Google is always at the top of all digital services. Their app engine has excellent uptime and supports many language packages, GitHub integration, and many other valuable integrations.
Key Features:
In a nutshell, traditional hosted development environments are far inferior to PaaS solutions. Simply put, traditional options don’t offer a lot of versatility or customization. At the same time, developers have to do most of the things themselves, including:
In other words, you have to do tons of work before you can start coding. Not only does PaaS remove all this work, but it also brings lots of other benefits, including:
The crucial difference between the two is that SaaS is a service that lets people use a particular software over the Internet. The provider manages the platform and its infrastructure. A good example is LiveAgent’s help desk software.
PaaS, on the other hand, is a whole environment that clients can use to manage, run, and develop applications. This is without having to worry about managing their operating systems.
Fundamentally, PaaS lets users manage data and applications making it perfect for companies, while SaaS is designed for end-users.
| Feature | SaaS | PaaS |
|---|---|---|
| Target User | End users | Developers |
| Primary Use | Using applications | Building applications |
| Management | Provider manages everything | Provider manages infrastructure |
| Customization | Limited | Extensive |
| Deployment | Ready to use | Requires development |
| Scalability | Automatic | Automatic |
| Cost Model | Subscription per user | Subscription per resource |
To better understand PaaS, it’s helpful to see how it fits within the broader cloud computing landscape:
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. You manage applications, data, runtime, middleware, and OS, while the provider manages virtualization, servers, storage, and networking.
Examples: AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine
PaaS provides a development platform in the cloud. You manage applications and data, while the provider manages everything else including runtime, middleware, OS, virtualization, servers, storage, and networking.
Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, IBM Cloud
SaaS provides ready-to-use applications over the internet. The provider manages everything, and you simply use the application.
Examples: Salesforce, Microsoft 365, LiveAgent
Platform as a Service represents a significant evolution in cloud computing, offering developers and businesses a powerful way to build, deploy, and manage applications without the burden of infrastructure management. By providing pre-built tools, automatic scaling, and comprehensive support, PaaS enables organizations to focus on innovation and delivering value to their customers.
Whether you’re a startup looking to launch quickly or an enterprise seeking to modernize your development processes, PaaS offers a flexible, cost-effective solution that can accelerate your time to market and improve your operational efficiency. As cloud technology continues to evolve, PaaS will likely play an increasingly important role in how organizations develop and deploy applications.
Ready to streamline your business operations? Discover how LiveAgent’s cloud-based help desk software can enhance your customer support while you focus on your core business development!
While you focus on building on PaaS, let LiveAgent handle your customer support. Cloud-based help desk software that just works.
Using a PaaS development environment is beneficial because companies get flexible integrations and services, robust capabilities, tons of database customization, multi-tenancy, customizable UI, and cloud computing infrastructure.
PaaS cloud components include the complete back-end infrastructure needed for app development. That includes networking infrastructure, storage options, computing resources, a variety of servers, database management tools, and BI services.
PaaS works as a cloud-based platform that delivers all the necessary development tools in an online environment with a customizable interface. The cloud environment lets users log in from any location, roll out products, test apps, and collaborate on projects.
There are countless models of cloud services and companies that provide them. Even though there isn't an exact number of PaaS solutions out there, we can freely say that their numbers exceed hundreds.
Some typical examples include IBM Cloud, Salesforce, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, and so on.
PaaS is far superior to internal software development environments. You can use these platforms on any device that has an Internet connection. They offer internal resources, network resources, and complete control over the development process with the initial investment.
SaaS is software people can use via a subscription-based app. PaaS is a whole infrastructure that comes with development tools used for creating cloud software.

Discover how cloud-based Contact Center as a Service (CCaaS) enhances customer support, lowers IT costs, and enables seamless omnichannel communication.

iCloud by Apple offers cloud storage and email services, seamlessly integrating with LiveAgent for organized customer communication. Simplify your help desk wit...

Discover the latest call center technology trends—cloud solutions, AI, omnichannel tools & more—to boost customer satisfaction & efficiency!