
Jitter Buffer
Learn how jitter buffers improve VoIP call quality by preventing choppy audio and resolving latency issues. Enhance your communication today!
Jitter VoIP affects call quality by causing delays and packet loss. Solutions include improving internet speed, configuring networks, using Ethernet, and setting quality of service. Aim for jitter under 30 ms for optimal VoIP performance.
VoIP technology converts the sounds of your voice into data called packets. These voice packets are then transmitted across the Internet and then converted back into the original sound.
Unfortunately, delays and problems sometimes impact the call. When packet loss occurs, your audio quality suffers. At best, a delay in packet transmission means short interruptions. At worst, packet jitter means entire words are lost. Fortunately, the loss of a single packet may not be noticeable. However, when more packets are lost, the entire packet stream might be disrupted. That means your conversation could be badly disrupted.

Network jitter refers to the amount of variation in the latency of receiving packets. For example, packet one arrives in 5 milliseconds, packet two arrives in 10 milliseconds, and packet three arrives in 30 milliseconds. In this example, network latency is gradually getting worse over time. If this happened to VoIP traffic, your conversation may become difficult to understand. It might be caused by high network congestion or inadequate VoIP speed due to a slow Internet connection.
All networks have network jitter to some degree. A small internal network like a private network of two computers in the same room would generally have close to zero network jitter. In contrast, a global company may have network connections in many different locations and, therefore, more jitter.

To understand how jitter issues result in poor call quality, it is helpful to understand the sources of jitter. Some causes of poor call quality may be easily fixed by your VoIP phone provider. Other poor voice quality causes, like a misconfigured router, may be more challenging.
Now that we’ve covered the technical overview, it’s time to cover an essential practical point. How exactly does excessive jitter impact your VoIP calls? There are two main ways jitter impacts your VoIP service.

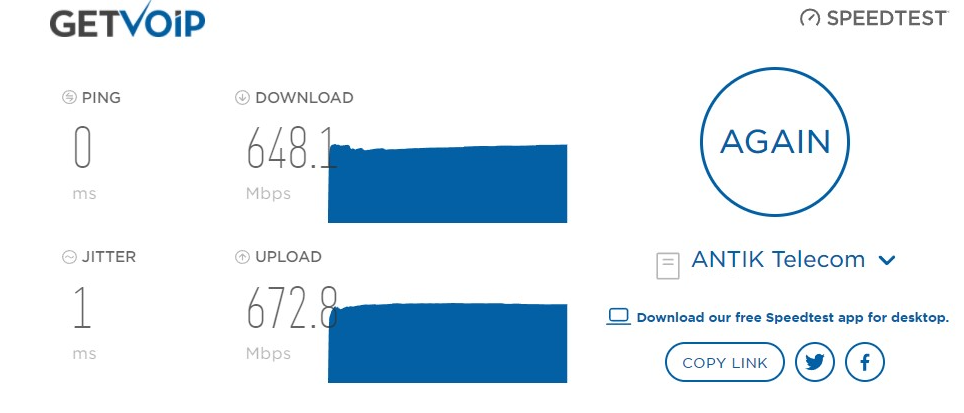
A very low level of jitter will have a minimal impact on your audio signal. It’s recommended to test your level of jitter before important calls. Fortunately, there are free bandwidth tests you can use to compare your network connection to industry standards.
Consider trying one of the following apps to run a network jitter test:
If you don’t want to use a specialized software tool, you can estimate jitter manually. Open a command window (in Windows, press the Windows key and type in CMD) and run a ping command to a website. You can then paste your results into a jitter calculator.
A good jitter score is less than 30 ms (i.e., 30 milliseconds).
Aim for a jitter of 30 milliseconds or less to avoid jitter issues while making calls on your VoIP service. To boost performance further, reduce your jitter as much as possible. For example, use quality of service (QoS) technology to prioritize VoIP calls.
Generally speaking, VoIP service may have problems when jitter goes above 30 milliseconds. To improve your call quality, there are a few areas you can look at:
There are several reasons for high jitter. Check all of these to successfully identify the issue:
There are a few ways to reduce jitter and get better VoIP calls:
Minimize jitter and deliver crystal-clear conversations with LiveAgent's reliable VoIP integrations and quality-optimized call center platform.
VoIP jitter is a problem that affects the quality of VoIP calls. It is defined as a variation in the delay of received packets during calls. When the delay in receiving packets is high, the call may have audio quality problems.
Network jitter is a situation where there is a significant variation in the latency of receiving packets. It can affect online gaming, video conferencing, and other Internet activities.
The leading causes of jitter include a misconfigured network, faulty hardware, and low Internet speeds. Jitter can also be caused by failing to use quality of service settings properly.
The main effects of jitter on VoIP calls include dropped calls, missing words, and service disruptions.
VoIP jitter is a difficult-to-understand conversation. You may not hear half the words spoken by the other person. Likewise, the person you are speaking to may not be able to hear you properly.
The easiest way to calculate jitter is to use a jitter software tool. For example, you can download the Solar winds jitter test app or the PRTG network monitor tool. Both of these tools offer free trials.
The acceptable jitter for VoIP calls is 30 milliseconds.
Your jitter may be high for several reasons. First, your Internet connection may be too slow to support VoIP calls. Second, there may be too many demands (e.g., online gaming, VoIP calls, video streaming, etc.) on your connection. Third, your router may not be configured to prioritize VoIP calls (i.e., quality of service settings).
There are a few easy ways to fix jitter for VoIP calls. Start by switching to an Ethernet cable because it offers higher speeds than wireless. Next, close non-VoIP programs during VoIP calls to maximize your bandwidth. If those steps do not help, try to use quality of service settings to prioritize your VoIP calls.

Learn how jitter buffers improve VoIP call quality by preventing choppy audio and resolving latency issues. Enhance your communication today!

Discover the essential components of VoIP infrastructure, including bandwidth, providers, and phones. Learn how LiveAgent can optimize VoIP for call centers and...

Traditional customer support replies slow you down. Discover how LiveAgent's AI Answer Improver boosts speed, quality, and satisfaction!